Views: 1 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2020-04-08 Origin: Site
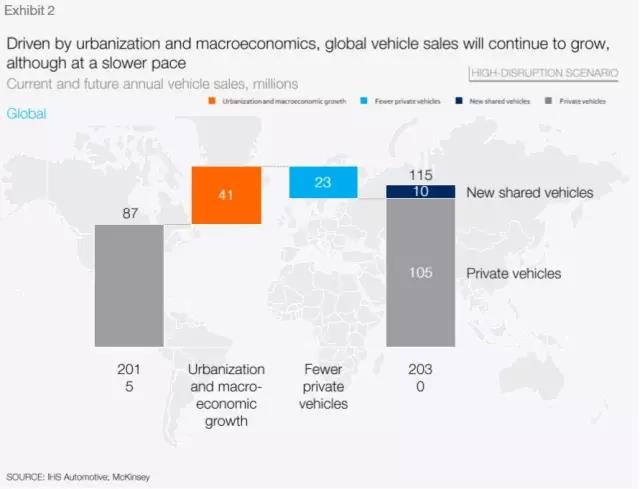
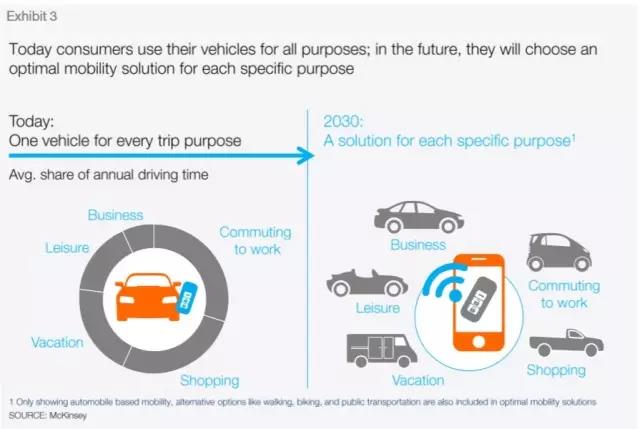
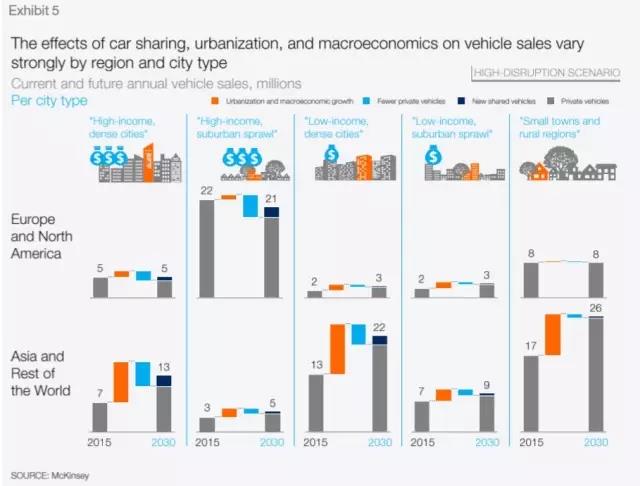
Technology-driven trends will completely change the way industry participants respond to changes in consumer behavior, develop partnerships, and drive transformational change. The development of emerging markets, the endless stream of new technologies, the introduction of sustainability policies, and changes in consumer preferences—all of these have changed the global economy dramatically. Digitalization, further automation, and new business models are transforming all industries, and the automotive industry is no exception. The above factors have led to four disruptive trends driven by technology in the automotive industry: diversified travel, autonomous driving, electrification, and intelligent interconnection. The automotive industry and experts agree that these four trends will strengthen and accelerate each other's influence. At the same time, the automotive industry is mature enough to make disruptive changes possible. Although it is generally believed that disruptive changes affecting the entire industry are beginning to take shape, there is no consensus on how these trends will affect the automotive industry in the next 10-15 years. To this end, we put forward eight perspectives of the\"2030 Automotive Revolution\", aiming to predict the changes that the automotive industry will usher in, as well as the changes to traditional car manufacturers and suppliers, potential new market participants, and regulators , Consumers, markets and industrial value chains. This study aims to make the upcoming changes more intuitive. Therefore, the predictions made in this study should be interpreted as the most likely speculations based on our understanding around the four major trends. Of course, these speculations are not decisive in nature, but by discussing the potential future, it should help industry participants better prepare for uncertainty. Transfer market and operating income 1. Driven by shared mobility, connected services and performance upgrades, the automotive industry's revenue will increase by 30% due to the new business model, or an increase of 1.5 trillion US dollars. The revenue of the automotive industry will increase substantially and diversify towards on-demand travel services and data-driven services. This will increase car sales revenue by an additional US $ 1.5 trillion in 2030, equivalent to a 30% increase. In the same period, revenue from traditional auto sales and after-sales products and services will reach US $ 5.2 trillion, a 50% increase from US $ 3.5 trillion in 2015. Intelligent interconnection and automation technology will make the car more and more a platform, allowing drivers and passengers to enjoy novel media forms and services during the journey, or to free up time for other personal activities. Innovation, especially the speed of software-based system innovation, will require cars to have upgradable features. With the increasing popularity of short-term shared travel, consumers will always understand the progress of technology, which will further increase the demand for upgradeable performance of private cars. 2. Although people are increasingly turning to shared travel, car sales will continue to increase, but only at a relatively low annual growth rate of 2%. Global car sales will continue to grow, but by 2030, sales growth will fall from 3.6% in the past five years to 2%. This is mainly due to the impact of the macro economy and the growth of travel services such as car sharing and online taxi calling. Detailed analysis shows that areas with high population density and long-term car ownership are fertile ground for these emerging mobility services, and many cities and suburbs in Europe and North America fall into this category. The new mobility service may lead to a decrease in private car sales, but this decrease may be offset by an increase in shared vehicle sales, because the latter has a higher utilization rate, greater wear and tear, and requires frequent replacement. Another factor contributing to the growth of global car sales is the good momentum of macroeconomic development, including the increase in global middle-class consumers. Due to the slowdown in growth in mature markets, global auto sales growth will continue to rely on emerging economies, especially China, and different product mixes have led to different revenue growth. Changes in mobility 3. The travel behavior of consumers is changing. By 2030, one out of every ten cars sold will be a shared car, and a travel solution customized based on user needs will also have a larger market. Factors such as changing consumer preferences, tightening regulatory measures, and technological breakthroughs have all caused major changes in personal travel. People are increasingly using multiple modes of transportation to complete travel, and goods and services are delivered to them rather than obtained by themselves. As a result, a series of diversified, on-demand travel plans will complement the traditional car sales model, especially in densely populated cities that discourage the use of private cars. Today's consumers use cars as a versatile tool for both commuting and family travel. In the future, they may want to be able to flexibly choose the best way to travel for a specific purpose and choose through a smartphone. We have noticed some signs that the importance of owning a private car is declining: in the United States, the proportion of young people (16-24 years old) holding a driver ’s license has dropped from 76% in 2000 to 71% in 2013, while in Over the past five years, the use of car-sharing services in North America and Germany has increased by more than 30% every year. The new habit of consumers choosing customized solutions according to different purposes will create special vehicles for specific purposes. For example, a car that provides online car-hailing services. This kind of car has a high usage rate, strong performance, can accumulate additional mileage, and has a higher passenger comfort. There are now millions of cars, and this is just the beginning. As a result of consumers turning to diversified mobility solutions, by 2030, one in every ten cars sold will be shared cars, which will reduce private car sales. This means that 30% of the mileage of newly sold vehicles comes from shared travel. According to this trend, by 2050, one out of every three cars sold may be a shared car. 4. The city type will replace the country or region and become a market segmentation dimension that determines travel behavior, that is, the speed and scope of the automotive revolution. To understand the future business opportunities, we need to examine the travel market from a more detailed perspective than in the past. Specifically, these markets need to be classified by city type, mainly depending on population density, economic development level, and prosperity. In all these market segments, consumer preferences, policies and regulations, and the availability and cost of new business models will vary greatly. For example, in a big city like London, owning a car is already a burden for many people, mainly because of the need to pay congestion fees, lack of parking spaces, traffic congestion and other factors. In contrast, in rural areas, such as Iowa in the United States, private cars are still the preferred mode of transportation so far. Therefore, the city type will replace the traditional approach of subdividing the travel market from a regional perspective and become an important indicator for examining travel behavior. By 2030, the auto market in New York State will likely be more similar to Shanghai than Kansas. High-tech diffusion 5. Once technical and regulatory issues are resolved, 15% of new cars sold in 2030 may be fully autonomous. It is unlikely that fully autonomous vehicles will be sold commercially by 2020. At the same time, the Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) will play an important role in helping regulators, consumers, and businesses prepare to gradually replace cars with drivers. The listing of ADAS has shown that the main challenges that hinder faster market penetration come from pricing, consumer perception, and safety / security issues. As for technical preparation, technology companies and startups may also play an important role in the development of autonomous vehicles. Regulation and consumer acceptance may be another obstacle to self-driving cars. However, once these issues are resolved, self-driving cars will bring tremendous value to consumers (for example, the ability to work while commuting, or conveniently use social media or watch movies on the go). Fully autonomous vehicles will gradually increase until they account for 15% of global passenger car sales in 2030. 6. The feasibility and competitiveness of electric vehicles are enhanced; however, the speed of consumer acceptance varies significantly in different regions. Tighter emission regulations, lower battery costs, more popular charging facilities and higher consumer acceptance will be the market for electric vehicles (hybrid, plug-in, battery electric and fuel cells) in the coming years Penetration creates new powerful forces. The speed of consumer acceptance will depend on the interaction between the pulling power of purchases (which is partly driven by the total cost of personally owned vehicles) and the driving force of regulation, which will vary significantly at different regional and local levels. By 2030, the proportion of electric vehicles may account for 10% to 50% of new car sales. The highest acceptance rate will be in developed densely populated cities, where there are strict emission regulations and consumer incentives (tax relief, special parking and driving privileges, preferential electricity prices, etc.). In small towns and rural areas, low-level charging infrastructure and a high degree of long-distance driving dependence will make the sales penetration rate low. Through continuous improvement of battery technology and costs, these local differences will be reduced, and electric vehicles are expected to gain more and more market share from the traditional car market. With the cost of batteries likely to drop from US $ 150 to US $ 200 per kWh in the next decade, electric vehicles will have cost competitiveness with traditional vehicles, which is the most important catalyst for market penetration. It is also worth noting that a large part of electric vehicles are hybrid vehicles, which means that even after 2030, the internal combustion engine will still occupy a place. 7. In a more complex and diversified industry pattern, existing manufacturers will be forced to compete in multiple fields simultaneously and cooperate with competitors. While other industries, such as telecommunications or mobile phone / cell phone industries, have been disrupted, the automotive industry still has only a few changes and integrations. For example, in the past 15 years, only two new companies have appeared in the top 15 list of automobile manufacturers (OEMs), while ten new companies have appeared in the mobile phone industry. The transformation of the travel industry into a service industry, coupled with the entry of new companies, will inevitably force traditional automakers to compete in multiple areas. Mobility service providers (such as Uber), technology giants (such as Apple and Google), and specialty car manufacturers (such as Tesla) have increased the complexity of the competitive landscape. Traditional auto companies are under constant pressure to reduce costs, improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and increase capital efficiency. They will feel a greater sense of urgency, and may transform their market positioning in the changing automotive and mobility industries, which may lead to existing Business combinations or new forms of cooperation. In the development of another subversive industry, software strength is increasingly becoming the industry's most important differentiating factor, involving multiple areas, including ADAS / active safety functions, intelligent interconnection and infotainment systems. In addition, with the development of Internet of Vehicles technology, automakers will have to participate in the new mobility ecosystem due to technology and consumer trends. 8. New market entrants will first focus on some profitable market segments and activities around the value chain, and then further explore more areas. Market diversification will bring opportunities for new companies. They will first focus on some links in the value chain, only targeting specific, profitable market segments, and then expand. Although Tesla, Google and Apple are currently showing great interest, we think they represent only the tip of the iceberg. There are more new companies that may enter the market, especially high-tech cash-rich companies and startups. These newly-entered companies from outside the industry also have greater influence on consumers and regulators (that is, to stimulate interest in new forms of travel and lobby for favorable regulatory measures for new technologies). Similarly, some Chinese automakers with impressive sales growth recently may use the current industry reshuffle to play an important role globally. future Existing auto companies cannot accurately predict the future of the industry. But they can take strategic measures at this stage to shape the development of the industry. To win in the inevitable reshuffle, existing companies need to take strategic measures in four areas: ①Against uncertainty: To succeed in 2030, auto companies must transform towards new market trends, explore alternative and complementary solutions to traditional business models, and explore new business models for the industry and their financial and consumer market feasibility. This requires auto companies to have strong planning capabilities and flexibility to identify and expand new excellent business models. ②Use of partnership: The automotive industry is transforming from peer competition to new competitive interactions, partnerships, and an open and scalable ecosystem. To succeed, automakers, suppliers, and service providers need to form alliances or participate in ecosystems—for example, exploring cooperation around infrastructure for autonomous vehicles and electric vehicles. ③Drive transformational change: As innovation and product value are increasingly defined by software, automakers need to adjust their skills and processes to meet new challenges such as software-led consumer value definition, network security, data privacy, and continuous product upgrades. ④Reshape the value proposition: Automakers must further differentiate their products / services and transform their value proposition from traditional auto sales and maintenance to integrated mobility services. This will place it in a more favorable position in the global growth of the automotive industry's revenue and total profit, sharing the revenue and profit growth brought by the new business model including online sales and travel services to the global automotive industry, while New business opportunities are catalyzed between the core automotive business and the new mobility business model. Conclusion
Source: McKinsey
Translator: Shen Danxi
Author: Paul Gao, Hans-Werner Kaas, Detlev Mohr, and Dominik Wee
Reorganized from the Industrial Innovation Think Tank
[Disclaimer] The article is to organize the article. If there are problems with the content and copyright of the work, please contact AI Auto Manufacturing within three hours of this article for deletion and communication.


